

Sesame seeds contain many of the same ingredients you’ll find in dietary supplements. So, all-in-all sesame seeds are a diabetes-friendly food that might help lower blood sugar. They also contain a compound called pinoresinol which might help control blood sugar by lowering glucose levels in the blood. Sesame seeds are a low carb, high protein food rich in healthy fats. Note: We need more studies on sesame seeds alone to prove the perks. In a 2014 study, researchers found the inflammation markers of people with kidney disease fell up to 79 percent in 3 months after eating a mix of sesame, flax, and pumpkin seeds daily. There’s some evidence to suggest that sesame seeds can help ease inflammation. But you can get around this by soaking, roasting, or sprouting your seeds. These antinutrients might reduce mineral absorption. Just keep in mind, raw sesame seeds contain compounds like oxalates and phytates. All of these nutrients can help support bone health. Sesame seeds are a great source of calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc. It also plays a big role in protein, bone, and DNA production. Additionally, magnesium helps your body regulate nerve function and blood sugar levels. Sesame seeds are a good source of magnesium, a mineral that can help lower blood pressure.

Studies show ALA may also help reduce your risk of heart disease. In addition to lignan - which can help block the absorption of cholesterol - sesame seeds contain alpha-linolenic acid (aka ALA). BTW, this is the “bad” type of cholesterol that can increase your risk of heart disease. Sesame seeds have been found to lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. But we need more research to show this is legit. They’re also rich in gamma-tocopherol, a form of vitamin E believed to reduce heart disease risk. These antioxidants can help protect your cells from damage and might reduce your risk of certain diseases. Sesame seeds contain plant compounds called lignans. Protein helps your body function in lots of important ways.
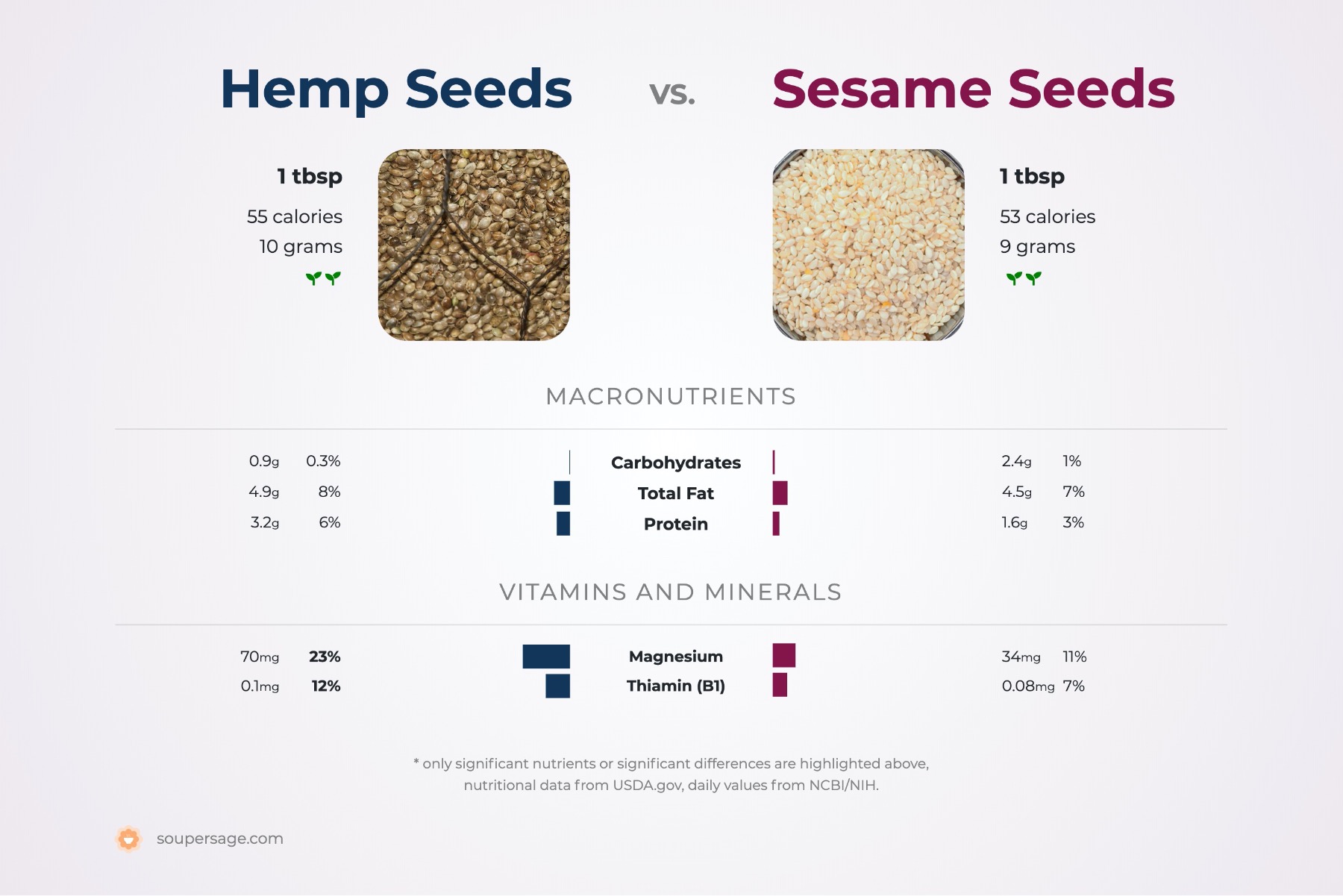
Vegetarians and vegans, rejoice! Sesame seeds are a potent source of plant protein. Research also shows vitamin B complex can help your brain function on fleek. That’s great news since these healthful nutrients help your body: Sesame seeds and their hulls are rich in B vitamins like thiamine, niacin, and vitamin B6. In 2 tablespoons of whole dried sesame seeds is an impressive 2.12 grams (g) of fiber. digestive conditions like diverticular diseaseĮating more sesame seeds is a great way to boost your fiber intake.Getting enough dietary fiber might reduce your risk of: Good source of fiberįiber isn’t just rad for regularity 💩. Here’s a rundown of the 10 best benefits. The amount of protein contained in both the seeds is exactly the same.Don’t let their size fool you. Sesame seeds do not contain any vitamin C but flaxseeds contain 0.6 mg of it which too is almost negligible. Sesame seeds contain 14.6 mg of iron whereas flaxseeds contain about 5.7 mg of iron content, making sesame a better option. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. Sesame (/ˈsɛzəmiː/ or /ˈsɛsəmiː/ Sesamum indicum) is a flowering plant in the genus Sesamum, also called benne. Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known. Sesame seeds are also used as an ingredient in soap, cosmetics, lubricants, and medicines. They are commonly added to certain foods to provide a nutty flavor and crunchy texture. Sesame seeds are rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
